Roulette
Roulette is a casino game named after a French diminutive for little wheel. In the game, players may choose to place bets on either a single number or a range of numbers, the colors red or black, or whether the number is odd or even.
To determine the winning number and color, a croupier spins a wheel in one direction, then spins a ball in the opposite direction around a tilted circular track running around the circumference of the wheel. The ball eventually loses momentum and falls on to the wheel and into one of 37 (in French/European roulette) or 38 (in American roulette) colored and numbered pockets on the wheel.[1]
History
The first form of roulette was devised in 18th century France. Blaise Pascal introduced a primitive form of roulette in the 17th century in his search for a perpetual motion machine.[2] The roulette wheel is believed to be a fusion of the English wheel games Roly-Poly, Reiner, Ace of Hearts, and E.O., the Italian board games of Hoca and Biribi, and "Roulette" from an already existing French board game of that name.
The game has been played in its present form since as early as 1796 in Paris. An early description of the roulette game in its current form is found in a French novel La Roulette, ou le Jour by Jaques Lablee, which describes a roulette wheel in the Palais Royal in Paris in 1796. The description included the house pockets, "There are exactly two slots reserved for the bank, whence it derives its sole mathematical advantage." It then goes on to describe the layout with, "...two betting spaces containing the bank's two numbers, zero and double zero." The book was published in 1801. An even earlier reference to a game of this name was published in regulations for New France (Québec) in 1758, which banned the games of "dice, hoca, faro, and roulette."[3]
The roulette wheels used in the casinos of Paris in the late 1790s had red for the single zero and black for the double zero. To avoid confusion, the color green was selected for the zeros in roulette wheels starting in the 1800s.
In 1843, in the German spa casino town of Homburg, fellow Frenchmen François and Louis Blanc introduced the single 0 style roulette wheel in order to compete against other casinos offering the traditional wheel with single and double zero house pockets.
In some forms of early American roulette wheels - as shown in the 1886 Hoyle gambling books, there were numbers 1 through 28, plus a single zero, a double zero, and an American Eagle. The Eagle slot, which was a symbol of American liberty, was a house slot that brought the casino extra edge. Soon, the tradition vanished and since then the wheel features only numbered slots.[4] Existing wheels with Eagle symbols are exceedingly rare, with fewer than a half-dozen copies known to exist. Authentic Eagled wheels in excellent condition can fetch tens of thousands of dollars at auction.
According to Hoyle "the single 0, the double 0, and eagle are never bars; but when the ball falls into either of them, the banker sweeps every thing upon the table, except what may happen to be bet on either one of them, when he pays twenty-seven for one, which is the amount paid for all sums bet upon any single figure."
In the 19th century, roulette spread all over Europe and the U.S.A., becoming one of the most famous and most popular casino games. When the German government abolished gambling in the 1860s, the Blanca family moved to the last legal remaining casino operation in Europe at Monte Carlo, where they established a gambling mecca for the elite of Europe. It was here that the single zero roulette wheel became the premier game, and over the years was exported around the world, except in the United States where the double zero wheel had remained dominant. Some call roulette the "King of Casino Games", probably because it was associated with the glamour of the casinos in Monte Carlo.
A legend says that François Blanc supposedly bargained with the devil to obtain the secrets of roulette. The legend is based on the fact that the sum of all the numbers on the roulette wheel (from 1 to 36) is 666, which is the "Number of the Beast".[5]
In the United States, the French double zero wheel made its way up the Mississippi from New Orleans, and then westward. It was here, because of rampant cheating by both operators and gamblers, that the wheel was eventually placed on top of the table to prevent devices being hidden in the table or wheel, and the betting layout was simplified. This eventually evolved into the American style roulette game as different from the traditional French game. The American game developed in the gambling dens across the new territories where makeshift games had been set up, whereas the French game evolved with style and leisure in Monte Carlo. However, it is the American style layout with its simplified betting and fast cash action, using either a single or double zero wheel, that now dominates in most casinos around the world.
During the first part of the 20th century, the only casino towns of note were Monte Carlo with the traditional single zero French wheel, and Las Vegas with the American double zero wheel. In the 1970s, casinos began to flourish around the world. By 2008 there were several hundred casinos world wide offering roulette games. The double zero wheel is found in the U.S., South America, and the Caribbean, while the single zero wheel is predominant elsewhere.
Rules of play against a casino
Roulette players have a variety of betting options. Placing inside bets is either selecting the exact number of the pocket the ball will land in, or a small range of pockets based on their proximity on the layout. Players wishing to bet on the 'outside' will select bets on larger positional groupings of pockets, the pocket color, or whether the winning number is odd or even.[6] The payout odds for each type of bet are based on its probability.
The roulette table usually imposes minimum and maximum bets, and these rules usually apply separately for all of a player's inside and outside bets for each spin. For inside bets at roulette tables, some casinos may use separate roulette table chips of various colors to distinguish players at the table. Players can continue to place bets as the ball spins around the wheel until the dealer announces no more bets or rien ne va plus.
When a winning number and color is determined by the roulette wheel, the dealer will place a marker also known as a dolly on that winning number on the roulette table layout. When the dolly is on the table, no players may place bets, collect bets, or remove any bets from the table. The dealer will then sweep away all other losing bets either by hand or rake, and determine all of the payouts to the remaining inside and outside winning bets. When the dealer is finished making payouts, the marker is removed from the board where players collect their winnings and make new bets. The winning chips remain on the board.
California Roulette
In 2004, California legalized a form of roulette known as California Roulette.[7] By law, the game must use cards and not slots on the roulette wheel to pick the winning number. There are at least two variations. In some casinos, the dealer spins a wheel containing 38 cards from 1 to 36, plus 0 and 00, and after betting is closed, stops the wheel; a pointer identifies the winning card, which the dealer removes and shows to the players. In the Cache Creek casino in northern California, a wheel resembling a traditional roulette wheel is used, but it has only alternating red and black slots with no numbers. As the ball is spinning, the dealer takes cards from a shoe and places two of them face down on the table in red and black rectangles. When the ball lands in a red or black slot, the card in the corresponding rectangle is turned over to reveal the winning number.
Roulette wheel number sequence
The pockets of the roulette wheel are numbered from 1 to 36.
In number ranges from 1 to 10 and 19 to 28, odd numbers are red and even are black. In ranges from 11 to 18 and 29 to 36, odd numbers are black and even are red.
There is a green pocket numbered 0 (zero). In American roulette, there is a second green pocket marked 00. Pocket number order on the roulette wheel adheres to the following clockwise sequence in most casinos:
- Single-zero wheel
- 0-32-15-19-4-21-2-25-17-34-6-27-13-36-11-30-8-23-10-5-24-16-33-1-20-14-31-9-22-18-29-7-28-12-35-3-26
- Double-zero wheel
- 0-28-9-26-30-11-7-20-32-17-5-22-34-15-3-24-36-13-1-00-27-10-25-29-12-8-19-31-18-6-21-33-16-4-23-35-14-2
Roulette table layout
The cloth covered betting area on a roulette table is known as the layout. The layout is either single zero or double zero. The European style layout has a single zero, and the American style layout is usually a double zero. The American style roulette table with a wheel at one end is now used in most casinos. The French style table with a wheel in the centre and a layout on either side is rarely found outside of Monte Carlo.
Types of bets
Inside bets
- Straight-up
- a single number bet. The chip is placed entirely on the middle of a number square.
- Split
- a bet on two adjoining numbers, either on the vertical or horizontal (as in 14-17 or 8-9). The chip is placed on the line between these numbers.
- Street
- a bet on three numbers on a single horizontal line. The chip is placed on the edge of the line of a number at the end of the line (either the left or the right, depending on the layout).
- Corner (or square)
- a bet on four numbers in a square layout (as in 11-12-14-15). The chip is placed at the horizontal and vertical intersection of the lines between the four numbers.
- Six line (or double street)
- a bet on two adjoining streets, with the chip placed at the corresponding intersection, as if in between where two street bets would be placed.
- Trio
- a bet on the intersecting point between 0, 1 and 2, or 0, 2 and 3 (single-zero layout only).
- Basket (or the first four)
- (non-square corner) a bet on 0, 1, 2, and 3 (single-zero layout only).
- Basket
- a bet on 0, 1, and 2; 0, 00, and 2; or 00, 2, and 3 (double-zero layout only). The chip is placed at the intersection of the three desired numbers.
- Top line
- a bet on 0, 00, 1, 2, and 3 (double-zero layout only). The chip is placed either at the corner of 0 and 1, or the corner of 00 and 3.
Outside bets
Outside bets typically have smaller payouts with better odds at winning.
- 1 to 18
- a bet on one of the first low eighteen numbers coming up.
- 19 to 36
- a bet on one of the latter high eighteen numbers coming up.
- Red or black
- a bet on which color the roulette wheel will show.
- Even or odd
- a bet on an even or odd nonzero number.
- Dozen bets
- a bet on the first (1-12), second (13-24), or third group (25-36) of twelve numbers.
- Column bets
- a bet on all 12 numbers on any of the three vertical lines (such as 1-4-7-10 on down to 34). The chip is placed on the space below the final number in this string.
- Snake Bet
- Essentially a special dozen bet consisting of a bet of the following numbers: 1, 5, 9, 12, 14, 16, 19, 23, 27, 30, 32, and 34. Some gambling "experts" consider it a so-called sucker bet as they claim that the player has to bet a unit on each of those numbers, yet this theory (as with many gambling theories) is not true as any bet on the table has exactly the same house edge. However, some casinos which allow the snake bet (not all casinos do) allow the table minimum to be bet on the snake by placing the bet on the lower corner of the 34 spot which touches the 19-36 even money bet.
In the UK, all bets have the same play to payout ratio; for instance, putting one chip on each number 1-12 will yield the same outcome as 12 chips on the first dozen (assuming the original stake is removed). The exception is the very outside bets (red/black, odd/even, low numbers/high numbers) when zero is the result only half of the original stake is captured by the dealer.
Bet odds table
(The initial bet is returned in addition to the mentioned payout.) The payout (for American and European roulette) can be calculated by:
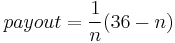
Where n is the number of squares the player is betting on.
| Bet name | Winning spaces | Payout | Odds against winning | Expected value (on a $1 bet) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 35 to 1 | 37 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| 00 | 00 | 35 to 1 | 37 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Straight up | Any single number | 35 to 1 | 37 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Row 00 | 0, 00 | 17 to 1 | 19 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Split | any two adjoining numbers vertical or horizontal | 17 to 1 | 19 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Basket | 0, 1, 2 or 00, 2, 3 or 0, 00, 2 | 11 to 1 | 11.667 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Street | any three numbers horizontal (1, 2, 3 or 4, 5, 6, etc.) | 11 to 1 | 11.667 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Corner | any four adjoining numbers in a block (1, 2, 4, 5 or 17, 18, 20, 21, etc.) | 8 to 1 | 8.5 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Top line | 0, 00, 1, 2, 3 | 6 to 1 | 6.6 to 1 | −$0.079 |
| Six line | any six numbers from two horizontal rows (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 or 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33 etc.) | 5 to 1 | 5.33 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| 1st column | 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, 22, 25, 28, 31, 34 | 2 to 1 | 2.167 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| 2nd column | 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23, 26, 29, 32, 35 | 2 to 1 | 2.167 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| 3rd column | 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36 | 2 to 1 | 2.167 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| 1st dozen | 1 through 12 | 2 to 1 | 2.167 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| 2nd dozen | 13 through 24 | 2 to 1 | 2.167 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| 3rd dozen | 25 through 36 | 2 to 1 | 2.167 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Odd | 1, 3, 5, ..., 35 | 1 to 1 | 1.111 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Even | 2, 4, 6, ..., 36 | 1 to 1 | 1.111 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Red | 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 12, 14, 16, 18, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 30, 32, 34, 36 |
1 to 1 | 1.111 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| Black | 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 11, 13, 15, 17, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 29, 31, 33, 35 |
1 to 1 | 1.111 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| 1 to 18 | 1, 2, 3, ..., 18 | 1 to 1 | 1.111 to 1 | −$0.053 |
| 19 to 36 | 19, 20, 21, ..., 36 | 1 to 1 | 1.111 to 1 | −$0.053 |
Note also that 0 and 00 are neither odd nor even in this game.
House edge
The house average or house edge (also called the expected value) is the amount the player loses relative for any bet made, on average. If a player bets on a single number in the American game there is a probability of 1/38 that the player wins 35 times the bet, and a 37/38 chance that the player loses their bet. The expected value is:
- −1×37⁄38 + 35×1⁄38 = −0.0526 (5.26% house edge)
For European roulette, a single number wins 1⁄37 and loses 36⁄37:
- −1×36⁄37 + 35×1/37 = −0.0270 (2.70% house edge)
The presence of the green squares on the roulette wheel and on the table are technically the only house edge. Outside bets will always lose when a single or double zero come up. However, the house also has an edge on inside bets because the pay outs are always set at 35 to 1 when you mathematically have a 37 to 1 chance at winning a straight bet on a single number. To demonstrate the house edge on inside bets, imagine placing straight $1 wagers on all inside numbers on a roulette table (including 0 and 00) to assure a win. You would only get back 36 times your original bet having spent $38. The only exception are the five numbers bet where the house edge is considerably higher (7.89% on an American wheel), and the 'even money' bets in some European games where the house edge is halved because only half the stake is lost when a zero comes up.
The house edge should not be confused with the hold. The hold is the average percentage of the money originally brought to the table that the player loses before he leaves - the actual "win" amount for the casino. The Casino Control Commission in Atlantic City releases a monthly report showing the win/hold amounts for each casino. The average win/hold for double zero wheels is between 21-30%, significantly more than the 5.26% house edge. This reflects the fact that the player is 'churning' the same money over and over again. A 23.6% hold, for example, would imply that on average, the player bets the total he brought to the table five times, as 23.6% is approximately equal to 100% - (100% - 5.26%)^5. For example, a player with $100 making $10 bets on red (which has a near 50/50 chance of winning) is highly unlikely to lose all his money after only 10 bets, and will most likely continue to bet until he has lost all of his money or decides to leave. A player making $10 bets on a single number (with only 1/38 chance of success) with a $100 bankroll is far more likely to lose all of his money after only 10 bets. Despite being more likely to lose, the casino's average hold from this type of player would be significantly lower than the even-money bettor, because the single number player will on average bet less money (at 5.26% expected loss per dollar bet).
In the early frontier gambling saloons, the house would set the odds on roulette tables at 27 for 1. This meant that on a $1 bet you would get $27 and the house would keep your initial dollar. Today most casino odds are set by law, and they have to be either 34 to 1 or 35 to 1. This means that the house pays you $34 or $35 and you get to keep your original $1 bet.
Mathematical model
As an example, we can examine the European roulette model (roulette with one zero). Since this roulette has 37 cells with equal odds of hitting, it is clear that this is a final model of field probability 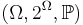 , where
, where 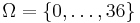 ,
, 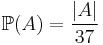 for all
for all 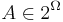 . We'll call the bet
. We'll call the bet 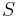 a three
a three 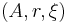 , where
, where  for a certain random event|event
for a certain random event|event 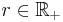 , and
, and 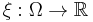 = random size. The event
= random size. The event  naturally leads to a winning event,
naturally leads to a winning event, 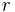 to the size of the bet (in dollars, for example),
to the size of the bet (in dollars, for example), 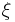 to the bet rule, and the mathematical expectation
to the bet rule, and the mathematical expectation ![M[\xi]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/2b4a3d11866d856ff274037693897356.png) relates to the bet profitability.
relates to the bet profitability.
The rules of European roulette have 10 types of bets. First we can examine the 'Straight Up' bet. It's clear that in this case, 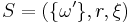 , where
, where 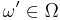 , and
, and 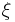 is determined by this law
is determined by this law
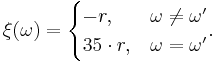
The bet's probability is equal to
![M[\xi] =
\frac{1}{37} \sum_{\omega \in \Omega} \xi(\omega) =
\frac{1}{37} \left(\xi(\omega^\prime) %2B
\sum_{\omega \ne \omega^\prime} \xi(\omega)\right) =
\frac{1}{37} \left(35 \cdot r - 36 \cdot r \right) = -\frac{r}{37}
\approx -0.027r.](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/a1c4a05105447575136f448fd8860fa7.png)
Without details, for a bet, red or black, the rule is determined as
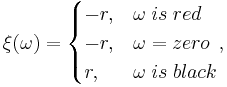
and the profitability ![M[\xi] = \frac{1}{37}(18 \cdot r - 18 \cdot r - r) = -\frac{r}{37}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/f5a95373f6ccb30fc39795fcbadc5bf0.png) . For similar reasons it is simple to see that the profitability is also equal for all remaining types of bets.
. For similar reasons it is simple to see that the profitability is also equal for all remaining types of bets. 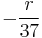 .[8]
.[8]
In reality this means that, the more bets a player makes, the more he is going to lose independent of the strategies (combinations of bet types or size of bets) that he employs:
![\sum_{n = 1}^{\infty}M[\xi_n] = -\frac{1}{37}\sum_{n = 1}^{\infty}r_n = -\infty.](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/96fba465aeb29fb7086f9bf398e7a823.png)
Here, the profit margin for the roulette owner is equal to approximately 2.7%. Nevethless, several roulette strategy systems have been developed despite the losing odds.[9]
It's worth noting that the odds for the player in American roulette are even worse, as the bet profitability is 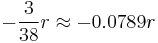 , and the rest are
, and the rest are 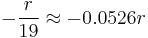 .
.
Called (or call) bets or announced bets
Although most often named "Call Bets" technically these bets are more accurately referred to as "announced bets". The legal distinction between a "Call Bet" and an "Announced Bet" is that a "Call Bet" is a bet called by the player without him placing any money on the table to cover the cost of the bet. In many jurisdictions (most notably the United Kingdom) this is considered gambling on credit and is illegal in some jurisdictions around the world. An "Announced Bet" is a bet called by the player for which he immediately places enough money to cover the amount of the bet on the table, prior to the outcome of the spin / hand in progress being known.
There are different number series in roulette that have special names attached to them. Most commonly these bets are known as "the French bets" and each covers a section of the wheel. For the sake of accuracy, Zero spiel although explained below is not a French bet, it is more accurately "the German bet". Players at a table may bet a set amount per series (or multiples of that amount). The series are based on the way certain numbers lie next to each other on the roulette wheel. Not all casinos offer these bets, and some may offer additional bets or variations on these.
Voisins du zéro (neighbors of zero)
This is a name, more accurately Grand Voisins du Zéro, for the seventeen numbers which lie between 22 and 25 on the wheel including 22 and 25 themselves. The series is 22,18,29,7,28,12,35,3,26,0,32,15,19,4,21,2,25 (on a single zero wheel).
9 chips or multiples thereof are bet. 2 chips are placed on the 0,2,3 trio; 1 on the 4/7 split; 1 on 12/15; 1 on 18/21; 1 on 19/22; 2 on 25/26/28/29 corner; and 1 on 32/35.
The bet on this section is very popular in Eastern Europe, most notably in the Czech Republic.
Jeu zéro (zero game)
Zero game, also known as zero spiel (spiel is German for game or play), is the name for the numbers closest to zero. All numbers in the zero game are included in the big series, but are placed differently. The numbers are as follows: 12, 35, 3, 26, 0, 32, 15.
The bet consists of 4 chips or multiples thereof. 1 chip on 0/3 split, 1 on 12-15 split, 1 on 26 straight up and 1 on 32-35 split. Popular bet in Germany and many European casinos. This bet is also offered as a 5 piece bet in many Eastern European casinos. As a 5 piece bet it is known as zero spiel naca and includes, in addition to the chips placed as noted above, a straight-up on number 19.
Le tiers du cylindre (Thirds of the wheel)
This is the name for the twelve numbers which lie on the opposite side of the wheel between 27 and 33 including 27 and 33 themselves. The series is 27,13,36,11,30,8,23,10,5,24,16,33 (on a single zero wheel). The full name (although very rarely used - most players just call it as "tiers") for this bet is "le tiers du cylindre" (translated from French into English means one third of the wheel) because it covers twelve numbers (placed as 6 splits), which is as close to 1/3 of the wheel as one can get. Very popular bet in British casinos. Tier bets out number Voisin and Orphans bets by a massive margin.
6 chips or multiples thereof are bet. 1 chip is placed on each of the following splits: 5/8; 10/11; 13/16; 23/24; 27/30; 33/36.
The Tiers bet is also called the "Small Series" and in some casinos (most notably in South Africa) "Series 5/8" It includes the following wagers which are all splits
- 5/8, 10/11, 13/16, 23/24, 27/30, 33/36
A variant known as "Tier 5,8,10,11" has an additional chip placed straight up on 5, 8, 10 and 11; and so is a 10-piece bet.
Orphelins (orphans)
These numbers make up the two slices of the wheel outside the Tiers and Voisins. They contain a total of eight numbers, comprising 17,34,6 and 1,20,14,31,9.
5 chips or multiples thereof are bet. 1 chip is placed straight-up on 1 and 1 chip on each of the splits: 6/9; 14/17; 17/20 and 31/34.
... and the neighbors
A number may be backed along with the 2 numbers on either side of it in a 5 piece bet. For example, "0 and the Neighbors" is a 5 piece bet with 1 piece straight-up on 3, 26, 0, 32 and 15. Neighbors bets are often put on in combinations, for example "1, 9, 14 and the neighbors" is a 15 piece bet covering 18, 22, 33, 16 with 1 piece; 9, 31, 20, 1 with 2 pieces and 14 with 3 pieces.
Any of the above bets may be combined, e.g. "Orphelins by 1 and Zero and the Neighbors by 1." The "...and the Neighbors." is often assumed by the croupier.
Final bets
Another bet offered on the single zero game is "finals". Most often pronounced finaal, but also finale (common with Italian speakers), and finals.
Finaal 4, for example, is a 4 piece bet and consists of 1 piece placed on each of the numbers ending in 4, that is 4, 14, 24 and 34. Finaal 7 is a 3 piece bet, 1 piece each on 7, 17 and 27.
Finaal bets from finaal 0 (zero) to finaal 6 cost 4 pieces. Finaal bets 7, 8 and 9 cost 3 pieces.
Some casinos also offer split-finaal bets, for example finaal 5/8 would be a 4 piece bet, 1 piece each on the splits 5/8, 15/18, 25/28 and 35.
Full completes/maximums
A complete bet places all of the inside bets on a certain number. Full complete bets are most often bet by high rollers as maximum bets.
The maximum amount allowed to be wagered on a single bet in European Roulette is based on a progressive betting model. If the casino allows a maximum bet of $1000 on a 35-1 straight-up, then on each 17-1 split connected to that straight-up $2000 may be wagered. Each 8-1 corner (covers four numbers) may have $4000 wagered on it. Each 11-1 street (covers three numbers) may have $3000 wagered on it. Each 5-1 sixline may have $6000 wagered on it. Each $1000 incremental bet would be represented by a token or "piece" that is used to specifically identify the player and the amount bet.
For instance, if a patron wished to place a full complete bet on 17, the player would call "17 to the maximum." This bet would require a total of 40 pieces or $40,000 dollars. To manually place the same wager, the player would need to bet:
| Bet Type | Number(s) bet On | Pieces | Amount Waged |
|---|---|---|---|
| Straight-Up | 17 | 1 | $1,000 |
| Split | 17, 14 | 2 | $2,000 |
| Split | 17, 16 | 2 | $2,000 |
| Split | 17, 18 | 2 | $2,000 |
| Split | 17, 20 | 2 | $2,000 |
| Street | 17, 16, 18 | 3 | $3,000 |
| Corner | 17, 16, 13, 14 | 4 | $4,000 |
| Corner | 17, 18, 14, 15 | 4 | $4,000 |
| Corner | 17, 16, 19, 20 | 4 | $4,000 |
| Corner | 17, 18, 20, 21 | 4 | $4,000 |
| Six Line | 17, 16, 18, 13, 14, 15 | 6 | $6,000 |
| Six Line | 17, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21 | 6 | $6,000 |
| Total Bets Placed | 40 | $40,000 |
The player calls his bet to the croupier (most often after the ball has been spun) and places enough chips to cover the bet on the table within reach of the croupier. The croupier will immediately announce the bet (repeat what the player has just said), ensure that the correct monetary amount has been given while simultaneously placing a matching markers on the number on the table and the amount wagered.
The payout for this bet if the chosen number wins is 392 pieces, in the case of a $1000 straight-up maximum, $40,000 bet, a payout of $392,000. The player's wagered 40 pieces, as with all winning bets in roulette, are still his property and in the absence of a request to the contrary are left up to possibly win again on the next spin.
Based on the location of the numbers on the layout, the number of chips required to "complete" a number can be determined.[10]
- Zero costs 17 pieces to complete and pays 235 pieces.
- Number 1 and number 3 each cost 27 pieces and pay 297 pieces.
- Number 2 is a 36 piece bet and pays 396 pieces.
- 1st column numbers 4 to 31 and 3rd column numbers 6 to 33, cost 30 pieces each to complete. The payout for a win on these 30 piece bets is 294 pieces.
- 2nd column numbers 5 to 32 cost 40 pieces each to complete. The payout for a win on these numbers is 392 pieces.
- Numbers 34 and 36 each cost 18 pieces and pay 198 pieces.
- Number 35 is a 24 piece bet which pays 264 pieces.
Most typically (Mayfair casinos in London and other top class European casinos) with these maximum or full complete bets nothing (except the aforementioned maximum button) is ever placed on the layout even in the case of a win. Experienced gaming staff, and the type of customers playing such bets, are fully aware of the payouts and so the croupier simply makes up the correct payout, announces its value to the table inspector (floor person in the USA) and the customer, and then passes it to the customer, but only after a verbal authorization from the inspector has been received.
Also typically at this level of play (house rules allowing) the experienced croupier caters to the needs of the customer and will most often add the customer's winning bet to the payout, as the type of player playing these bets very rarely bets the same number two spins in succession. For example, the winning 40 piece / $40,000 bet on "17 to the maximum" pays 392 pieces / $392,000. The experienced croupier would pay the player 432 pieces / $432,000, that is 392 + 40, with the announcement that the payout "is with your bet down Sir".
There are also several methods to determine the payout should a number adjacent to a chosen number be the winner; for example, player bets 40 pieces on "23 to the maximum" and number 26 is the winning number. The most notable method is known as the "station" system or method. When paying in stations, the dealer counts the number of ways or stations that the winning number hits the complete bet. In the example above, 26 hits four stations – two different corners, one split and one six-line. The dealer takes the number four, multiplies it by 35 and adds the original four to the payout. 4x35=140, 140+4=144. Thus the payout is 144 with the players bet down.
In some casinos, a player may bet full complete for less than the table straight-up maximum; for example, "number 17 full complete by $25" would cost $1000, that is 40 pieces each at $25 value.[11]
Betting strategies and tactics
Over the years, many people have tried to beat the casino, and turn roulette - a game designed to turn a profit for the house - into one on which the player expects to win. Most of the time this comes down to the use of betting systems, strategies which say that the house edge can be beaten by simply employing a special pattern of bets, often relying on the "Gambler's fallacy", the idea that past results are any guide to the future (for example, if a roulette wheel has come up 10 times in a row on red, that red on the next spin is any more or less likely than if the last spin was black).
All betting systems that rely on patterns, when employed on casino edge games will result, on average, in the player losing money.[12] In practice, players employing betting systems may win, and may indeed win very large sums of money, but the losses (which, depending on the design of the betting system, may occur quite rarely) will outweigh the wins. Certain systems, such as the Martingale, described below, are extremely risky, because the worst case scenario (which is mathematically certain to happen, at some point) may see the player chasing losses with ever bigger bets until he runs out of money.
At least in the 1930s, some professional gamblers were able to consistently gain an edge in roulette by seeking out rigged wheels (not difficult to find at that time) and betting opposite the largest bets.
Biased wheels
Whereas betting systems are essentially an attempt to beat the fact that a geometric series with initial value of 0.95 (American roulette) or 0.97 (European roulette) will inevitably over time tend to zero, engineers instead attempt to overcome the house edge through predicting the mechanical performance of the wheel, most notably by Joseph Jagger at Monte Carlo in 1873. These schemes work by determining that the ball is more likely to fall at certain numbers, and if sufficiently good will raise the return of the game above 100%, defeating the betting system problem.
In the early 1990s, Gonzalo Garcia-Pelayo believed that casino roulette wheels were not perfectly random, and that by recording the results and analysing them with a computer, he could gain an edge on the house by predicting that certain numbers were more likely to occur next than the 1-in-36 odds offered by the house suggested. This he did at the Casino de Madrid in Madrid, Spain, winning 600,000 euros in a single day, and one million euros in total. Legal action against him by the casino was unsuccessful, it being ruled that the casino should fix its wheel.[13][14]
To prevent exploits like these, the casinos monitor the performance of their wheels, and rebalance and realign them regularly to try to keep the result of the spins as uniform as possible.
In 1982, several casinos in Britain began to lose large sums of money at their roulette tables to teams of gamblers from the USA. Upon investigation by the police, it was discovered they were using a legal system of biased wheel-section betting. As a result of this, the British roulette wheel manufacturer John Huxley manufactured a roulette wheel to counteract the problem.
The new wheel, designed by George Melas, was called "low profile" because the pockets had been drastically reduced in depth, and various other design modifications caused the ball to descend in a gradual approach to the pocket area. In 1986, when a professional gambling team headed by Billy Walters won $3.8 million using the system on an old wheel at the Golden Nugget in Atlantic City, every casino in the world took notice, and within one year had switched to the new low-profile wheel.
Edward O. Thorp (the developer of card counting and an early hedge-fund pioneer) and Claude Shannon (a mathematician and electronic engineer best known for his contributions to information theory) built arguably the first wearable computer to predict the landing of the ball in 1961. This system worked by timing the ball and wheel, and using the information obtained to calculate the most likely octant where the ball would fall. Ironically, this technique works best with an unbiased wheel though it could still be countered quite easily by simply closing the table for betting before beginning the spin.
Thomas Bass, in his book The Eudaemonic Pie 1991 (published as The Newtonian Casino in Britain), has claimed to be able to predict wheel performance in real time. The book describes the exploits of a group of University of California Santa Cruz students, who called themselves the Eudaemons, who in the late 1970s used computers in their shoes to win at roulette. This is an updated and improved version of Edward O Thorp's approach where Newtonian Laws of Motion are applied to track the roulette ball's deceleration, hence the title.
In 2004 it was reported that a group of two Serbs and one Hungarian in London had used a laser scanner hidden inside a mobile phone linked to a computer to predict the sector of the wheel where the ball was most likely to drop.[15] They were arrested, but released without charge as there was no proof they had technically interfered with casino equipment.[16]
Specific betting systems
The numerous even-money bets in roulette have inspired many players over the years to attempt to beat the game by using one or more variations of a Martingale betting strategy, wherein the gamer doubles the bet after every loss, so that the first win would recover all previous losses, plus win a profit equal to the original bet. The problem with this strategy is that, remembering that past results do not affect the future, it is possible for the player to lose so many times in a row, that the player, doubling and redoubling his bets, either runs out of money or hits the table limit. A large financial loss is certain in the long term if the player continued to employ this strategy. Another strategy is the Fibonacci system, where bets are calculated according to the Fibonacci sequence. Regardless of the specific progression, no such strategy can statistically overcome the casino's advantage, since the expected value of each allowed bet is negative.
While not a strategy to win money, former Los Angeles Times editor Andrés Martinez described a betting method in his book on Las Vegas titled "24/7". He called it the "dopey experiment". The idea is to divide one's roulette session bankroll into 35 units. This unit is bet on a particular number for 35 consecutive spins. Thus, if the number hits in that time, the gambler wins back the original bankroll and can play subsequent spins with house money. However, there is only a 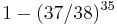 = 60.68% probability of winning within 35 spins (assuming a double-zero wheel with 38 pockets).
= 60.68% probability of winning within 35 spins (assuming a double-zero wheel with 38 pockets).
Labouchère System
The Labouchère System is a progression betting strategy like the Martingale but does not require the gambler to risk his stake as quickly with dramatic double-ups. The Labouchere System involves using a series of numbers in a line to determine the bet amount, following a win or a loss. Typically, the player adds the numbers at the front and end of the line to determine the size of the next bet. When he wins, he crosses out numbers and continues working on the smaller line. If he loses, then he adds his previous bet to the end of the line and continues to work on the longer line. This is a much more flexible progression betting system and there is much room for the player to design his initial line to his own playing preference.
This system is one that is designed so that when the player has won over a third of his bets (less than the expected 18/38), he will win. Whereas the Martingale will cause ruin in the event of a long sequence of successive losses, the Labouchère system will cause bet size to grow quickly even where a losing sequence is broken by wins. This occurs because as the player loses, the average bet size in the line increases.
As with all other betting systems, the average value of this system is negative.
D'Alembert System
The system, also called montant et demontant (from French, meaning upwards and downwards), is often called a pyramid system. It is based on a mathematical equilibrium theory devised by a French mathematician of the same name. Like the Martingale, this system is mainly applied to the even-money outside bets, and is favored by players who want to keep the amount of their bets and losses to a minimum. The betting progression is very simple: After each loss, one unit is added to the next bet, and after each win, one unit is deducted from the next bet. Starting with an initial bet of, say, 10 units, a loss would raise the next bet to 11 units. If this is followed by a win, the next bet would be 10 units. Another win would lower the next bet to 9 units.
This betting system relies on the gambler's fallacy - that the player is more likely to lose following a win, and more likely win following a loss.[17]
Other systems
There are numerous other betting systems that rely on this fallacy, or that attempt to follow 'streaks' (looking for patterns in randomness), varying bet size accordingly.
Many betting systems are sold online, and may make outlandish promises that the player can 'beat' the system by following them. One such system was advertised by Jason Gillon of Rotherham, UK, who claimed you could 'earn £200 daily' by following his betting system, described as a 'loophole'. As the system was advertised in the UK press, it was subject to Advertising Standards Authority regulation, and following a complaint, it was ruled by the ASA that Mr. Gillon had failed to support his claims you could earn £200 daily, and that he had failed to show that there was any loophole.[18]
Using the dozen bet
There are two versions to this system, single-dozen bets and double-dozen bets. In the single-dozen-bet version, the player uses a progressively incrementing stake list starting from the casino table minimum, to the table maximum. The aim here is to use a single-dozen bet to win before the stake list ends. Many techniques are employed such as: betting on the same dozen to appear after two consecutive appearances, betting on the dozen that has appeared most in the last 15, 9, or 5 spins, betting on the dozen that, after a long absence of 7 or more spins, appears for the first time. The double-dozen bet version uses two dozen bets and half the stake list size of the single-dozen-bet version.
Real-life roulette exploits
- In 1873, Briton Joseph Jaggers made the first famous biased roulette wheel exploit. Mr. Jaggers, with a team of six accomplices, carefully observed all the wheels at the Monte Carlo casino and found one wheel with significant bias. By taking advantage of this flaw they managed to win over $325,000, an astronomical sum in 1873.[19]
- In the summer of 1891 at the Monte Carlo casino, a part-time swindler and petty crook from London named Charles Wells broke the bank at each table he played over a period of several days. Breaking the bank meant he won all the available money in the table bank that day, and a black cloth would be placed over the table until the bank was replenished. In song and life, he was celebrated as "The Man That Broke the Bank at Monte Carlo".
- In 1992 in Gdynia (Poland) in Jackpol Casino, Paweł Piskorski (Polish politician, former Secretary General of Platforma Obywatelska and Member of European Parliament, today Leader of Stronnictwo Demokratyczne) claimed to have won 4,950,000,000 zloty (approximately $175,000 today). This, at least, was the explanation he gave to the revenue office for his income that year. The claim is implausible, because the house maximum at that time was 1,000,000 zloty: he would have had to have won 138 times in succession, with each bet set at the house maximum.
- In 2004, Ashley Revell of London sold all of his possessions, clothing included, and placed his entire net worth of US$135,300 on red at the Plaza Hotel in Las Vegas. The ball landed on "Red 7" and Revell walked away with $270,600.
- On 2 October 2009, Derren Brown (as part of his controversial "The Events" series) bet £5000 of a member of the public's money on a single number of a roulette wheel somewhere in Europe. This was shown live across the UK using a camera hidden in Brown's sleeve. His plan was to use the laws of physics to predict where the ball would end up, based upon the speed of the wheel and the ball. Brown took approximately three seconds after the wheel started spinning to place his £5000 bet on the number 8, only to see it land on 30 - just one number out.
In film
- In the 1942 film Casablanca, Rick's Café Americain has a trick roulette wheel. Rick (played by Humphrey Bogart) uncharacteristically takes pity on a young Bulgarian refugee couple. The husband has lost most of his money at roulette, trying to win enough to bribe police captain Renault. Rick suggests the man bet on 22. After the number comes up, Rick tells him to let it all ride. He does, and wins again. Rick tells him to cash in his winnings ... and never come back.
- In the 1971 Western comedy Support Your Local Gunfighter, James Garner's character has a gambling addiction - he cannot stop betting everything he has on a single roulette spin. He loses several times, but finally wins at the very end.
- Near the beginning of the 1973 film The Sting, Johnny Hooker (Robert Redford) takes his share of the money conned from a numbers runner and loses nearly all of it on a single bet against a rigged roulette wheel.
- In the third part of the 1998 film Run, Lola, Run, Lola (Franka Potente) uses all her money to buy a 100-mark chip. (She is actually just short of 100 marks, but gains the sympathy of a casino employee who gives her the chip for what money she has.) She bets her single chip on 20 and wins. She lets her winnings ride on 20 and wins again, making her total winnings 129,600 marks (29,600 more than her smuggler boyfriend owed his boss, Ronnie). The odds of two consecutive wins on a European roulette wheel are exactly 1368-to-1 against.
- In the 2010 film "Fast and Furious 5*, Don Omar and Tego Calderon play roulette and each bet their millions on red or black. The ball lands on green.
- Players should not collect their winnings and betting chips on the outside chances until all of the winnings in the same box (e.g., all bets and winnings on 'red') have been paid. This is to avoid confusion and minimize the chance for players to steal other players' chips.
- Players must not touch chips after the dealer gives the hand signal or announces "no more bets". Players are not allowed to remove, change or add bets past this point.
- When the dealer has placed the dolly (the plastic marker used to mark the winning number) it is strictly prohibited to touch any chips on a winning chance.
- Dealers are not allowed to take money to change for chips from a player's hand. If the player wishes to get more chips, he or she must place the money on the layout of the table.
- The use of electronic equipment, such as mobile phones and cameras, at the table is also prohibited.
- The only items allowed in front of a player are chips, money, drinks, and cigarettes. Bulky items such as wallets and purses or bags must not be on the table.
Common etiquette practices
- Players should place chips on the board rather than tossing them. Tossed chips may displace other bets or roll down to the "chipping machine". If the player cannot reach to place a bet himself, he/she should announce the bet to the dealer. This is treated as any other call bet.
- Changes for cash or color chips are supposed to be done in between spins. If the dealer has time, he will make changes during the spin, but he/she will most likely prioritize call bets before changes.
- All call bets are considered courtesy bets and are only placed if the dealer has time to change and place the bets. The bet is considered taken only if the dealer and the inspector dealer has repeated the bet. If the dealer does not take the bet, he/she will announce "no bet". To argue with the dealer about which bets have been taken is considered extremely impolite and will most likely render a warning from the inspector dealer or pit boss.
- No food or drink is allowed over the table.
See also
- Smart Live Casino
- Bauernroulette
- Eudaemons
- Live Roulette TV
- Monte Carlo Paradox
- Russian roulette
- Straperlo
Notes
- ^ "Expectations for Roulette" by Michael Schreiber, Wolfram Demonstrations Project, demonstrations.wolfram.com.
- ^ MIT, "Inventor of the Week Archive: Pascal: Mechanical Calculator", May 2003. "Pascal worked on many versions of the devices, leading to his attempt to create a perpetual motion machine. He has been credited with introducing the roulette machine, which was a by-product of these experiments."
- ^ Roulette Wheel Study, Ron Shelley, (1988)
- ^ "History of Roulette Game". RouletteDoc.com. http://roulettedoc.com/history-of-roulette.htm. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- ^ The last term in a sequence of partial sums composed of either sequence is 666, the "beast number".
- ^ The Mathematics of Roulette Betting - complex bets, profit-function, equivalence of bets , probability.infarom.ro.
- ^ California Roulette and California Craps as House-Banked Card Games
- ^ Roulette Math, en.wikibooks.org
- ^ Roulette System, betvoyager.com.
- ^ http://www.wheelroulette.com/roulette-call-max.html
- ^ http://www.wheelroulette.com/roulette-call-max.html
- ^ Wizardofodds.com
- ^ Theage.com.au
- ^ Wheel of Fortune | Motley Fool, fool.com
- ^ The sting: did gang really use a laser, phone and a computer to take the Ritz for £1.3m? | Science | The Guardian, guardian.co.uk
- ^ Ritz Roulette £1.3m win scam | Casino news | Gambling News at Online Gambling Directory, gamblinggates.com
- ^ Roulette Systems, roulettehero.com
- ^ ASA.org.uk
- ^ Joseph Jaggers, gamblershandbook.net
External links
- Roulette at the Open Directory Project